What is Lighting?
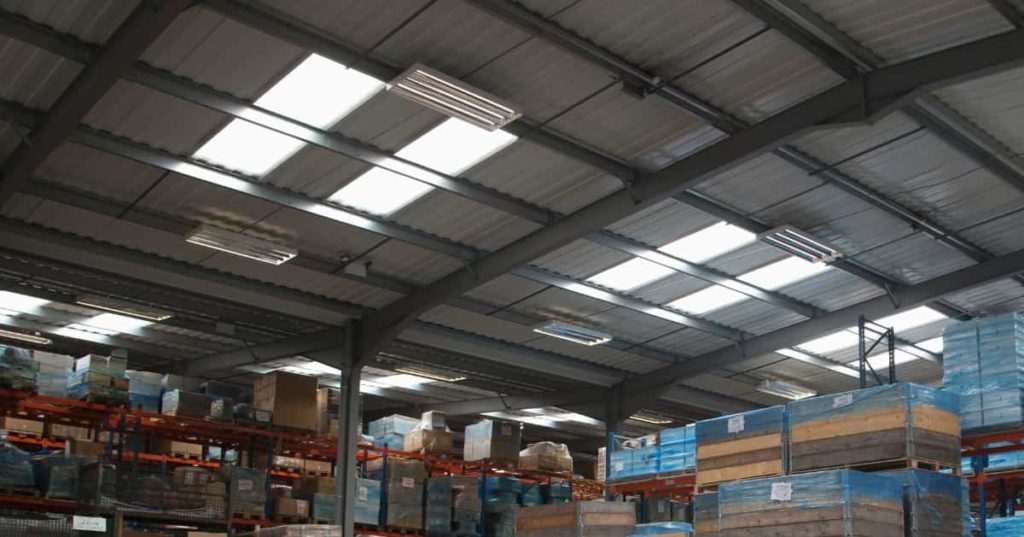
Lighting or illumination uses natural or artificial light in spaces to get the desired aesthetic or functional effect. Architects for green factories use windows, skylights and other methods to optimise natural lighting. Additionally, well-planned lighting on a shopfloor or any workspace in an industrial facility helps improve performance and aesthetics.
Furthermore, green rating and certification systems like IGBC, GRIHA, and LEED have points for daylighting, renewable energy sources and energy-efficient systems in the factory. That is another reason for Industrial architects to use natural lighting as a significant light source.
What is meant by natural lighting?
The light from the sun is natural lighting. Industrial design architects ensure natural lighting in industries through skylights and windows. While natural light is generated naturally, artificial light is produced through electrical equipment. As natural lighting helps reduce the requirement for artificial light in the facility, energy saving is an additional benefit.
Natural lighting is a significant aspect of design. National Building Codes of India Part 8, Section 1 Lighting and ventilation recommends the values of illuminance for each activity in an industry. Furthermore, the architects for green factories decide the positioning and direction of a building based on maximising natural lighting.
The benefits of natural lighting are:
- Natural lighting enhances space utilisation.
- The natural lighting provides a good ambience.
- The workforce has lesser health issues as compared with artificial lighting.
- Natural lighting reduces the consumption of electricity by providing general and task lighting.
However, industrial architects have to plan the design to ensure diffused light. These days there are daylight systems available in the market that allow diffuse sunlight to reach the interiors of a building.
What is passive daylighting?
Passive lighting is a non-mechanical element in a building that uses systems to bring sunlight to light up the interiors. Some examples of passive daylighting are windows, skylights, tubes, and glass doors. Active lighting, on the contrary, is a mechanical system that tracks and/ or follows the sun and delivers sunlight to the interiors of a building.
To conclude, Architects for green factories use natural daylighting for an energy-efficient and sustainable factory. Additionally, a green factory is sustainable and improves branding.