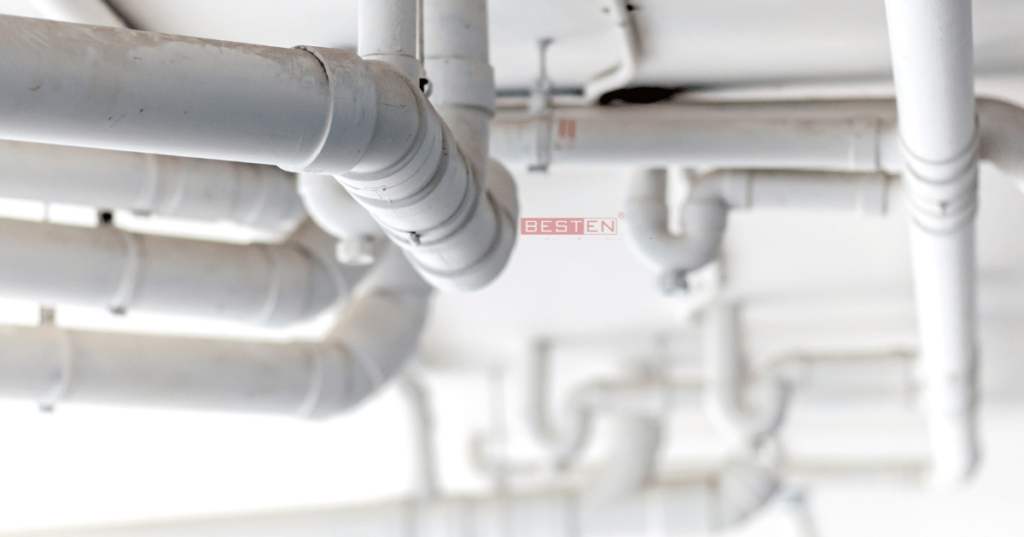
Plumbing and sanitation design plays a critical role in the functionality, safety, and environmental impact of industries. Plumbing consultants ensure for maintaining hygiene, complying with regulations, and ensuring the safety of workers a proper plumbing system is designed.
Factories often have unique requirements and challenges due to the scale and types of processes and materials being handled.
Uses
The plumbing systems have a complex network of systems for:
- Potable water supply: It helps deliver clean, safe water for various purposes, including drinking, washing, and industrial applications. Depending on the source and desired water quality, the system may also include water treatment systems like filtration or reverse osmosis.
- Sanitary drainage: The plumbing system efficiently removes wastewater from toilets, sinks, showers, and other fixtures. Additionally, proper ventilation is crucial and helps prevent the build-up of harmful gases and ensure efficient flow.
- Process water supply: The system also caters to the needs of various industrial processes, such as specific quality parameters like temperature, pressure, or chemical composition, necessitating dedicated treatment or heating/cooling systems.
- Industrial wastewater disposal: The system also includes safely treating and disposing wastewater generated by industrial processes. The consultants also ensure that the treatment is in place before discharge as per local regulations and environmental impact considerations.
Key Factors that plumbing consultants consider while designing
The key factors influence the design of these systems in industrial settings:
- Water quality: Different areas within a facility may have varying water quality requirements. While stringent regulations govern potable water for human consumption, at the same time, process water quality differs based on its use, such as cooling equipment or washing industrial components.
- Water demand: The consultants typically design a system based on peak water usage to ensure sufficient supply throughout the facility. So, the team must analyse the water consumption patterns across different departments and processes.
- Drainage capacity: The drainage system must be appropriately designed to handle the expected volume of wastewater without causing blockages or overflows. The number of fixtures, flow rates, and the potential presence of solids or hazardous materials influence the design.
- Material selection: Longevity and compatibility with the fluids transmitted help select the right materials for pipes and fittings. Factors like pressure, temperature, and potential corrosion resistance of the materials also help in material selection.
- Maintenance: The design must prioritise easy access to critical components for routine maintenance, repairs, and potential future modifications.
- Compliance with regulations: Adherence to relevant local regulations is essential. Furthermore, this compliance ensures environmental protection, worker safety, and adherence to established safety protocols.
- Risk Assessment: The consultants undertake a thorough risk assessment is necessary to identify potential hazards associated with plumbing and sanitation systems in industrial facilities. Risks may include chemical contamination, biohazards, and physical hazards such as high-pressure water or steam.
- Backflow Prevention: Backflow prevention devices prevent the contamination of potable water sources by backflow from industrial processes or non-potable water systems.
- Emergency: There must be emergency response plans in place for plumbing and sanitation-related incidents, such as chemical spills, leaks, or equipment failures.
- Integration with Facility Design: The plumbing consultants must coordinate plumbing and sanitation design with the overall facility layout and infrastructure. As a result, the design ensures optimisation, efficiency and minimal conflicts with other systems such as HVAC, electrical, and process piping.
Some industries, like food and beverages, need a specific and meticulous approach to sanitation. The plumbing system must minimise the risk of cross-contamination by appropriate measures. Some measures include hot water loops, proper backflow prevention devices, and easily cleanable surfaces. Similarly, chemical industries need plumbing systems with containment measures, waste segregation, and corrosion-resistant materials to avoid environmental pollution.
Conclusion
Plumbing consultants meticulously consider these diverse factors. They tailor the design to the specific needs of each facility. Plumbing consultants can create efficient, safe, and environmentally responsible plumbing and sanitation systems. As a result, these systems support the smooth operation and well-being of occupants while adhering to relevant regulations.