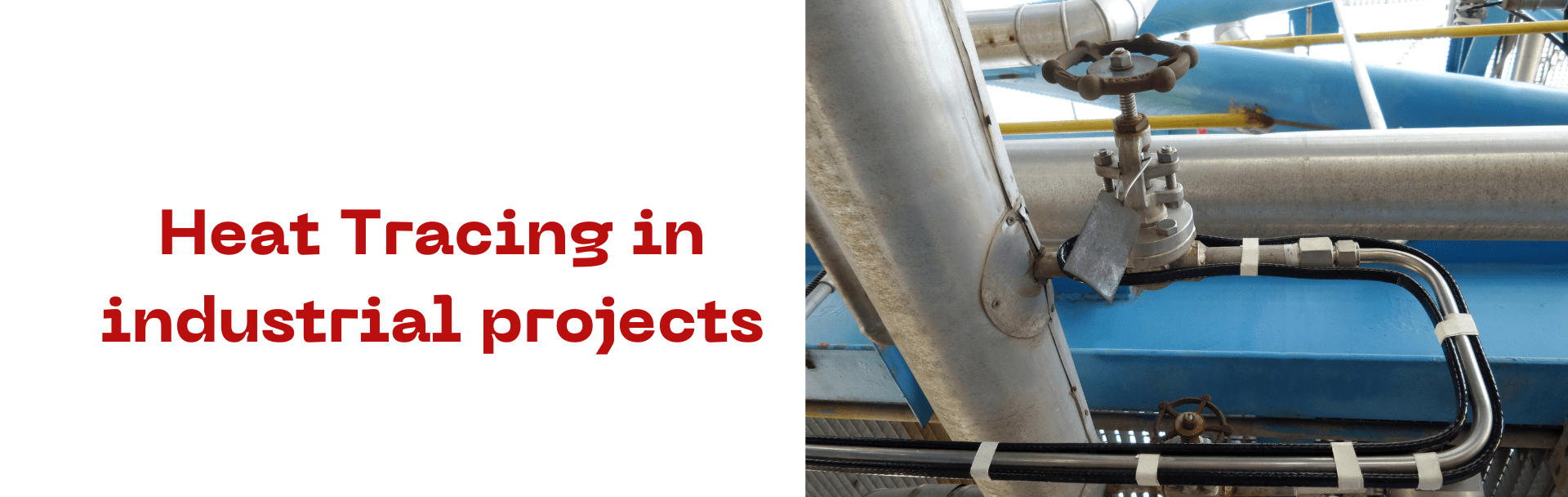
Heat Tracing in industrial projects
Heat tracing in industries is a system in industrial piping to raise and maintain the temperature of fluids. It is critical in industrial processes, serving as a reliable and efficient method to maintain desired temperatures. Heat tracing helps prevent freezing, solidification, or viscosity changes. This tracing helps MEP consultants ensure product quality, process efficiency, and safety.
Types of heat tracing?
- Steam Tracing: Steam tracing is a heating method that enables pipelines to maintain process fluids at a specified elevated temperature. So, this method is for industries adversely affected by cold conditions or temperature dips. Also, this tracing is used to maintain product viscosity, avoid chemical separation, and avoid gas condensation. The heat tracing methods consist of fluid heating and electric heating. This process includes the installation of smaller dia steam pipelines in direct contact with the process pipelines and carry steam controlled at a certain temperature.
- Electric heat tracing: This method of heat tracing uses heating through elements in cables and strips. Electrical heat tracing is recommended in hazardous areas or where steam is not readily available.
- Fluid heat tracing: This tracing works by circulating a heated fluid through the tracer piping system. This method is efficient when the piping system is for long distances.
What are the key considerations for heat tracing?
- Temperature control: The selection should consider the capability of the system to maintain the required temperature range. The temperature sensors and controllers help maintain temperature.
- Energy efficiency: It helps to select a system that is energy efficient. A proper insulation and piping sizing are a must.
- Safety Factors: The consultants must ensure safety systems in place to avoid incidents such as burns, scalds, or electrical shocks.
- Corrosion: In industries that are prone to corrosion, the heating elements and tracer pipe materials must be selected accordingly with resistant to corrosion.
- Expansion and contraction: The MEP consultants must desing the system to accommodate the expansion and contraction of the tracer pipes due to temperature changes. This can be achieved through the use of expansion loops or flexible connectors.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is a mustl to ensure the optimal and continued performance of the heat tracing system. This includes inspecting the system for damage, cleaning tracer pipes, and calibrating temperature sensors.
What are the applications of heat tracing?
Heat tracing is also recommended for
- Pharma industries: Heat tracing helps to maintain the temperature of pipelines and storage tanks for sensitive drugs and chemicals.
- Food industries: Freezing of food is a concern during transportation and storage. Heat tracing helps in such condition also.
- Chemical processing: Heat tracing helps to control the viscosity and flow properties of chemical substances.
Benefits of heat tracing in industries
The benefits of heat tracing are as follows:
- It ensures consistent temperature and improves process reliability. As a result, it reduces downtime and improves overall process stability.
- Heat tracing improves product quality by avoiding temperature-related defects.
- The maintenance costs are down as heat tracing helps avoid freezing or solidification.
- Safety of the system is improved due as heat tracing prevents development of hazardous conditions.
- It helps increase productivity.
Heat tracing is a versatile and essential technology that MEP consultants can design and implement to meet specific process requirements.
What are the factors for consideration by MEP Consultants in Heat/Steam Tracing?
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) consultants use their expertise to design safe, efficient systems that meet the project requirements. Some of the essential factors are:
- Process Requirements and Temperature Profiles: Consultants have to understand the process, identify critical areas and develop temperature profiles before designing the system.
- Pipe Material and Insulation: The selection of proper material and insulation is also in the purview of the MEP consultants.
- Tracing Method Selection: Moreover, the consultants have to evaluate various options for tracing and recommend an efficient method suitable for the process.
- Tracer Layout and Spacing: The design of the entire tracing system including routing, clearances, maintenance accessibility has to be designed.
- Temperature Control and Monitoring: The selection of appropriate sensors, temperature controllers and monitoring systems is also an essential part of the tracing system.
- Safety Considerations: Safety systems should be in place.
- Energy Efficiency: The design of the system should ensure energy efficiency and avoid heat loss.
Furthermore, MEP consultants can design and implement heat/steam tracing systems that are reliable, efficient, and safe for the intended application.
To conclude, no other form of trace heating offers the multiple benefits of steam in terms of efficiency, low operating costs, controllability, flexibility and safety in industrial projects.