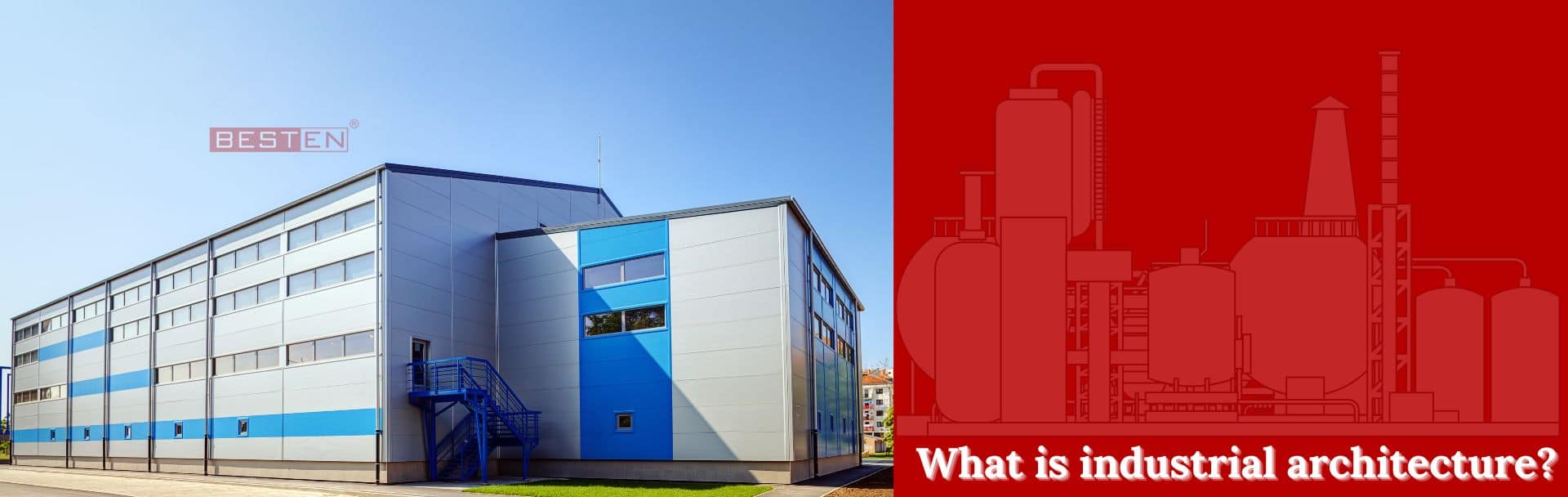
What is industrial architecture?
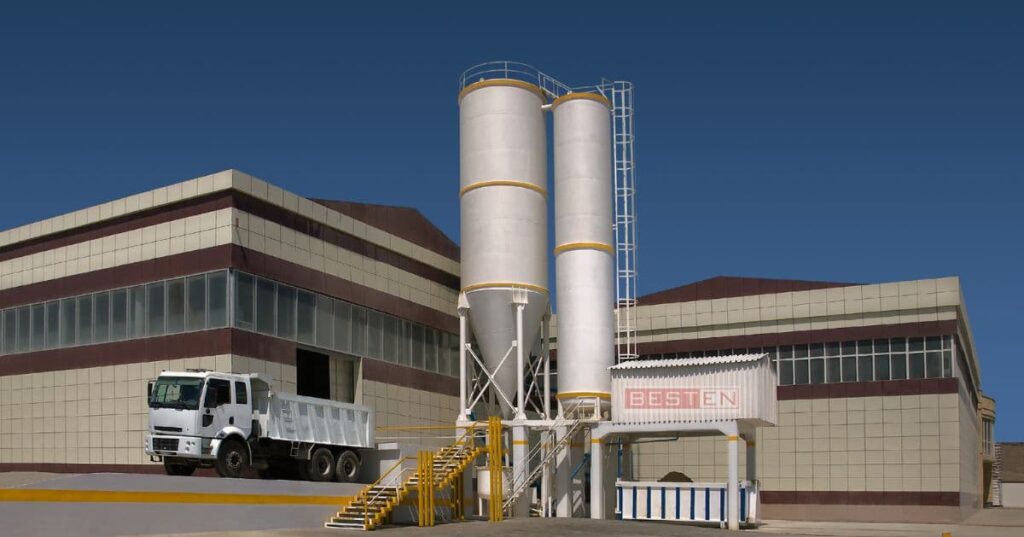
Industrial architecture involves creating buildings that cater to the industry’s needs. Architects and engineers include factories, warehouses, power plants, distilleries and breweries, refineries, grain silos, steel mills and similar facilities in industrial architecture.
Industrial architecture focuses on functionality, efficiency, space, cost optimisation, and aesthetics.
What is Functionality?
Functionality refers to how well the building satisfies the users’ objectives. This involves the efficiency of the process and activities inside the building. Multiple factors influence functionality, such as the process, number of users, lighting, ventilation, safety, comfort, and compliance. The architecture and design of a building influence the efficiency of a process.
In industries, functionality is the primary objective, i.e., prioritising the process within the building over other architectural factors. It also means that the industrial architecture essential has a simple design, and practicality is important.
Features of functionality in industrial architecture
Some of the features of functionality include:
- Interiors: the space allocation is based on machinery, production layout and storage areas.
- Materials: The architects and engineers choose materials like steel, concrete, and bricks that can withstand industrial operations. These materials ensure low maintenance.
- Lighting: Incorporating natural lighting, skylight panels, and daylight panels help provide an ambient atmosphere to the workforce. It also helps bring down electricity expenses.
- Ventilation: Architects must incorporate ventilation per the local regulatory guidelines for industries. A well-ventilated workplace is known to enhance productivity. Additionally, energy efficiency is an advantage.
- Sustainability: Green buildings reduce environmental impact through sustainable practices and materials. Renewable energy, water-saving fixtures, and energy-efficient fittings also contribute to sustainability.
- Optimised process flow to ensure smooth workflow, material movement, and man movement.
Importance of functionality in industrial architecture
The following factors show the importance of functionality in industries:
- A properly designed industrial space brings economic benefits. The process is optimised, and there is no waste or dead space. Functionality proportionately increases productivity and output.
- Functionality includes safety, so workers’ safety, clear walkways, and designated area allocation are all part of the design.
- Durable materials that withstand industrial operations have a longer life span.
- Occupant satisfaction: a functional building often contributes to improved workforce satisfaction and reduced workforce turnover.
- Compliance: An essential aspect of functionality is incorporating design features according to codes and regulations, such as structural integrity, fire safety, and accessibility. Well-experienced architects incorporate compliance requirements like emergency exits and fire escape routes in the design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, functionality is the cornerstone of efficient and safe industrial workspaces. In these functional buildings, sustainability and compliance also play a significant role in ensuring cost-effective operations. Architects and engineers, with their expertise, strike a delicate balance between functionality and aesthetics, creating visually appealing, sustainable, and highly functional industrial buildings.